Progress in Psoriasis Treatment:Do You Know the New Treatment Options
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition characterized by red, itchy, and scaly patches. It can significantly impact the quality of life, but advancements in medical research have led to the development of new and effective treatments. Here's a comprehensive guide to understanding the latest treatment options for psoriasis.
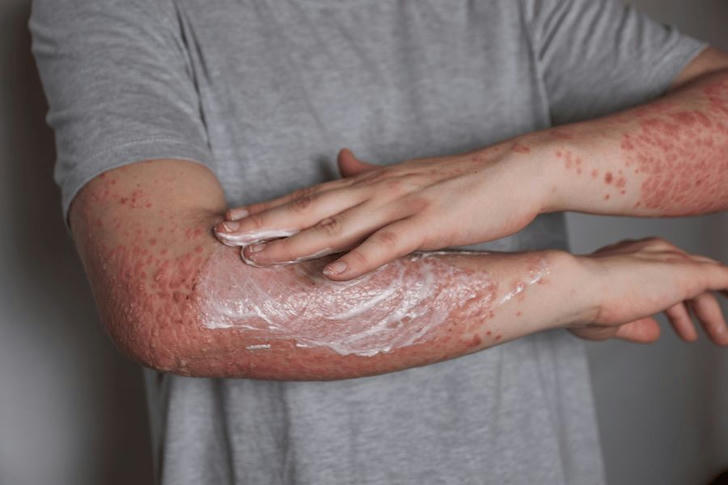
Understanding Psoriasis
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease that causes rapid skin cell turnover, leading to the build-up of thick, scaly patches on the skin. Common types include plaque psoriasis, guttate psoriasis, inverse psoriasis, pustular psoriasis, and erythrodermic psoriasis. Treatments aim to reduce inflammation, slow down skin cell production, and manage symptoms.
Traditional Treatments
Topical Treatments:
Corticosteroids: Reduce inflammation and relieve itching.
Vitamin D Analogues: Slow down skin cell growth.
Retinoids: Normalize skin cell growth.
Phototherapy:
UVB Therapy: Uses ultraviolet light B to slow skin cell production.
PUVA Therapy: Combines psoralen (a drug that makes skin more sensitive to light) with UVA light.
Systemic Treatments:
Methotrexate: Suppresses the immune system.
Cyclosporine: Suppresses the immune system.
Acitretin: A retinoid for severe cases.
New and Emerging Treatments
Biologics:
TNF-alpha Inhibitors: Block tumor necrosis factor-alpha, a substance involved in systemic inflammation (e.g., Infliximab, Adalimumab).
IL-17 Inhibitors: Target interleukin-17, a cytokine involved in inflammation (e.g., Secukinumab, Ixekizumab).
IL-23 Inhibitors: Target interleukin-23, another cytokine involved in the inflammatory process (e.g., Guselkumab, Risankizumab).
IL-12/23 Inhibitors: Target both interleukin-12 and interleukin-23 (e.g., Ustekinumab).
Small Molecule Inhibitors:
PDE4 Inhibitors: Block phosphodiesterase 4 to reduce inflammation (e.g., Apremilast).
JAK Inhibitors: Target Janus kinase enzymes to interfere with the inflammatory process (e.g., Tofacitinib).
Topical Non-Steroidal Treatments:
Tapinarof: A topical aryl hydrocarbon receptor modulating agent that reduces inflammation and regulates skin cell growth.
Roflumilast: A topical PDE4 inhibitor specifically formulated for psoriasis.
Combination Therapies
Combining treatments can enhance efficacy and minimize side effects. Examples include:
Topical + Phototherapy: Using topical treatments in conjunction with phototherapy for better results.
Biologics + Topical Treatments: Combining biologics with topical treatments to target different aspects of the disease.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle changes and home remedies can help manage psoriasis:
Moisturizing Regularly: Keeps skin hydrated and reduces itching.
Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding triggers such as stress, smoking, and certain foods.
Dietary Adjustments: Anti-inflammatory diets may help reduce symptoms.
Stress Management: Techniques like yoga, meditation, and exercise can reduce stress, a known trigger for psoriasis flare-ups.
Personalized Medicine and Future Directions
Advancements in genetic research and personalized medicine are paving the way for more targeted and effective treatments. Future directions include:
Genetic Testing: Identifying genetic markers to predict treatment response.
Precision Medicine: Tailoring treatments based on individual genetic profiles and disease characteristics.
Conclusion
The landscape of psoriasis treatment has significantly evolved, offering new hope for those affected by this chronic condition. By understanding the latest treatment options and working closely with healthcare providers, patients can find effective strategies to manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. Always consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.
